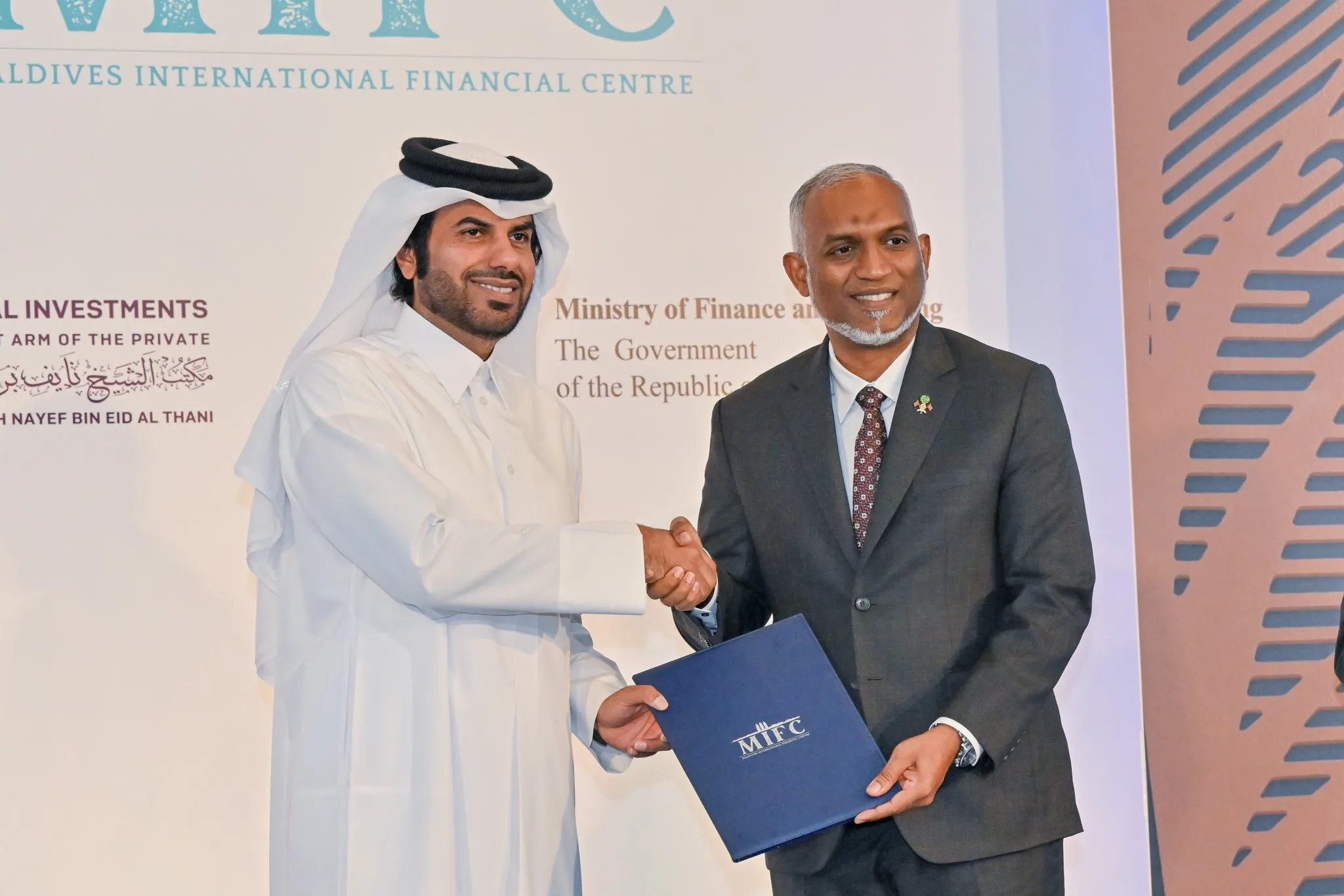
The Maldives, long known for its breathtaking resorts and vibrant tourism industry, is now setting its sights on a new frontier: becoming a global financial hub. The Maldives International Financial Centre (MIFC) is a monumental $8.8 billion joint venture between the Maldivian government and MBS Global Investments, a Dubai-based entity backed by Qatari royal interests. This project, scheduled for completion by 2030, promises to reshape the country’s economic landscape. It aims to diversify its dependence on tourism and establish the Maldives as a major player in global finance and innovation.
A Vision for Transformation
MIFC centers on a vision to transform the Maldives into a leading financial and technology hub in the Indian Ocean. The financial free zone, spanning 780,000 square meters in Hulhumalé, will attract fintech firms, international financial institutions, and digital entrepreneurs. Its business-friendly environment offers incentives such as zero corporate tax, tax-free inheritance, no residency requirements, and guaranteed foreign ownership, positioning MIFC as a unique proposition for global investors.
This digital-first financial ecosystem will host a range of services, including offshore private banking, green finance, digital assets, and multi-currency banking. The district will also feature world-class infrastructure: high-rise towers, branded residences, luxury hotels, retail space, and a state-of-the-art convention center that will host 35,000 visitors daily. This comprehensive vision will create 16,000 new jobs and position the Maldives as a competitive player in global markets by 2040.
A Strategic Investment for Growth
MIFC is not just about infrastructure; it aims to position the Maldives as an emerging leader in the world of finance. The government has outlined ambitious economic goals, including generating over $1 billion in annual revenue within the first five years of operation. This effort seeks to reduce the country’s economic vulnerability, which currently relies heavily on tourism while facing mounting external debt.
For the Maldives, this project goes beyond business; it represents a statement of intent to diversify its economy and reduce the risks associated with its single-industry focus. By tapping into global financial networks and attracting investors from around the world, MIFC can pave the way for sustainable economic growth and long-term prosperity.
Geopolitical and Economic Implications
MBS Global Investments, backed by Qatari royalty, lends the project significant geopolitical weight. Positioned strategically between two regional giants, India and China, the Maldives aims to capitalize on its political neutrality and become a financial bridge between East and West. The proximity to major shipping lanes and key economic corridors enhances the region’s strategic importance, making MIFC not only an economic endeavor but a geopolitical one as well.
By diversifying and strengthening its economy, the Maldives hopes to attract global capital that might otherwise flow to competing projects in the region. With its focus on sustainability and cutting-edge financial technologies, MIFC positions itself as a forward-looking alternative, appealing to investors seeking stability and long-term growth.
Criticism and Controversy
However, the project has faced criticism. Opposition voices have raised concerns about the transparency of the partnership with MBS Global Investments, particularly regarding the company’s lack of verifiable financial records and audit transparency. They have also questioned the credibility of its leadership and the potential risks associated with such a large-scale venture backed by a single foreign investor.
While these concerns are valid, the scale and ambition of the MIFC project remain undeniable. The Maldives government has committed to ensuring the project adheres to global standards of governance, and its focus remains on delivering a financial center that supports innovation and economic growth.
Looking Forward
MIFC represents an exciting leap into the future of finance and innovation for the Maldives. It is a bold attempt to build a resilient, diversified economy that can thrive long after the tourism boom. As the project progresses toward its 2030 completion, it will be interesting to see how it shapes the region’s financial landscape and whether it can overcome the challenges posed by its critics. For now, the Maldives is positioning itself as a key player in the rapidly evolving global financial scene, and MIFC could become the catalyst for a new era of growth and prosperity.