It has been eight weeks since Maldives declared State of Public Health Emergency. While the government has been taking several measures to strengthen the fight against COVID-19, the next couple of weeks will be crucial to the Maldives.
Considering the rate at which positive cases are increasing, it is assumed that the country will reach peak by the end of May 2020. The National Emergency Operations Center (NEOC) has warned that the situation could get worse within the next two weeks. Health professionals have made projections of the spread of the virus and has estimated that the Maldives may suffer over 77,000 cases of COVID-19 in total. Research Analyst Dr. Sheena Moosa formed these projections and presented during a press conference stressing on the need to revise the current testing capacity. According to her, authorities may be able to identify about 390 cases on the peak day while in reality, around 1500 cases may occur.
The first positive case in Male’ City on 15th April 2020 led to the greater Male’ Area being under lockdown as an attempt to contain the spread. However, the virus has spread to some of the other residential islands. Although the islands are not under strict lockdown, the residents have been asked to maintain social distancing, avoid public gatherings and banned from inter-island travelling without approval.
Currently, Maldives has confirmed 790 cases of COVID-19 with majority of the infected individuals being foreigners. The country has witnessed 03 deceased due to the virus with two of them being Maldivians and one Bangladeshi. As of yet, the island nation has recorded 29 recoveries.
Frontline workers being at high-risk, 05 police officer as well as a number of MNDF officers are among the infected. In addition to those, some delivery personals as well as some WAMCO staff were also tested positive for COVID-19. While this has created panic among the people, majority of the public has been adhering to the advice of the authorities and relevant figures.
As the majority of the cases are Bangladeshi and Indian workers, the risk of more migrant workers being infected are high. Hence, the countries’ governments have been working towards repatriation. On 08th May 2020, an Indian naval vessel departed from the Maldives with 698 Indian nationals who were left stranded in the country due to the pandemic. An additional group of Indians will be evacuated on 10th April 2020.
A number of repatriation flights have also been conducted within the past few days to repatriate foreigners stuck in Maldives. This includes flights conducted by Srilankan Airlines, Turkish Airlines, and Skyup Airlines.
Strengthening Healthcare Systems
The government has also been establishing additional quarantine and isolation facilities due to the surge in numbers. This includes Gulhee Falhu quarantine facility with the capacity to accommodate 5000 individuals as well as Hulhumale’ quarantine center.
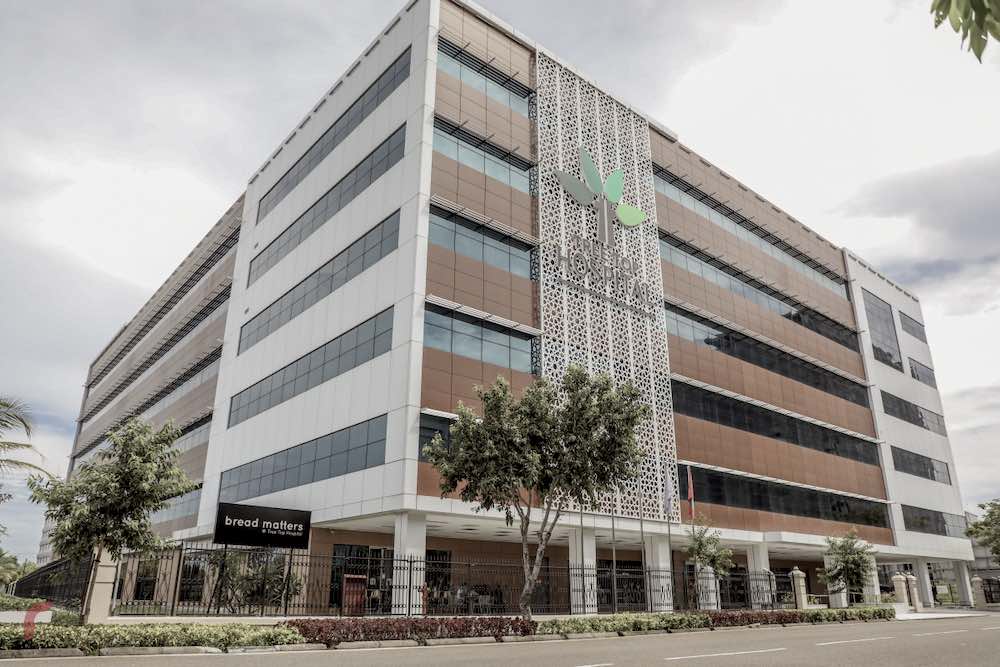
Furthermore, private hospital Tree Top Hospital has been offered to the government to entirely dedicate the facility for treating COVID-19 patients for three months. The hospital is well equipped with the capacity to treat up to 180 COVID-19 patients at any given time.
Economic Challenges and Recovery Plans
President Ibrahim Solih had set up a resilience and recovery task force to prepare for the reopening of Maldives’ economy post COVID-19. The National Task Force aims to formulate strategies in close coordination with relevant stakeholders in order to revive the country’s economy with combined efforts to boost the economic growth. While the task force will be overseen by the president, it includes working groups on finance, economic recovery and social sector.
Despite the nation’s economy smashed to the ground due to the pandemic, the government has been taking several measures to ease the struggles of the people.
With a number of individuals currently unemployed with no sources of income, the government had introduced stimulus grants to support those affected by the pandemic. On 07th May 2020, the government announced the disbursement of MVR 70 million as relief loans. SMEs and Self-employed individuals facing cashflow constraints can avail these funds through SDFC. A grant scheme for artists and freelancers affected by the situation will also be introduced soon.
However, Maldives Association of Tourism Industry (MATI) has criticized the government for the lack of timely actions and job losses in the tourism industry. Revealing that the current relief packages were not formulated in consultation with them, MATI added that the challenges faced by the industry needs to be addressed urgently in order to recover from the impact of COVID-19.
Whilst the government of Maldives has emphasized on the reopening of borders in July. Being the backbone of the country’s economy, the recovery and resumption of the tourism industry is vital to rise from the economic fall.
Hopeful of combating the pandemic with stronger precautionary measures being implemented, Maldives looks forward to overcoming the pandemic and opening its shores again.